
WELCOME TO KNOWLEDGE CENTER
Q.1. – What is Share Market in simple words?
Share market is a collection of markets where stocks (pieces of ownership in a company) are bought and sold. It allows companies to raise money by selling shares to the public and allows investors to buy and sell shares in those companies.
Types of Share Market-
There are two kinds of Share Markets – Primary and Second Markets.
Primary Market: This where a company gets registered to issue a certain amount of shares and raise money. This is also called getting listed in a stock exchange.
Secondary Market: Secondary market transactions are referred to trades where one investor buys shares from another investor at the prevailing market price or at whatever price the two parties agree upon.
Q.2. – Why Invest in Share Market?
Ans :- We invest in shares to build our wealth in the long run. While some people view shares to be a risky investment, many studies have proved that put
Q.3. – What are SENSEX and NIFTY?
Ans : – The S&P BSE SENSEX and the Nifty 50 are two of the most widely followed stock market indices in India. These indices are considered to be barometers of the Indian economy and are used to measure the performance of the Indian stock market.
The S&P BSE SENSEX, also known as the BSE 30, comprises 30 of the largest and most actively traded stocks listed on the Bombay Stock Exchange (BSE) in India
The Nifty 50, also known as the Nifty, comprises of 50 of the largest and most actively traded stocks listed on the National Stock Exchange of India (NSE)
Both the SENSEX and Nifty are widely followed by investors, analysts, and economists as a measure of the overall performance of the Indian stock market. They are considered key indicators of the health of the Indian economy and are used by investors to make investment decisions.
ting your money in the right shares for a long period of time (five to 10 years) can provide inflation-beating returns — and be a better investment option than real estate and gold.
What is a Bear Market?
A bear market is when the buyers are pessimistic about the rise in the prices of the shares and the sellers outnumber the buyers in the market. A bear market is due to the economy not doing very well; the GDP levels are falling, unemployment is high, and there is a fair chance that recession is approaching. When the investors are pessimistic, they tend to sell their shares rather than buy new ones and thus, are called “Bears.”
What is a Bull Market?
A bull market is the condition of a financial market in which prices are rising or are expected to rise. The term”Bull Market” is most often used to refer to the stock market but can be applied to anything that is traded, such as bonds, real estate, currencies, and commodities.

What is Limit Order?
A limit order in the financial markets is a direction to purchase or sell a stock or other security at a specified price or better. This stipulation allows traders to better control the prices at which they trade. A limit can be placed on either a buy or a sell order:
- A buy limit order will be executed only at the limit price or a lower price.
- A sell limit order will be executed only at the limit price or a higher one.
What Is a IPO?
IPO means Initial Public Offering. It is a process by which a privately held company becomes a publicly-traded company by offering its shares to the public for the first time. A private company that has a handful of shareholders shares the ownership by going public by trading its shares. Through the IPO, the company gets its name listed on the stock exchange
What Is a Blue Chip?
A blue chip is a nationally or internationally recognized, well-established, and financially sound company that is publicly traded. Blue chips generally sell high-quality, widely accepted products and services.
What is Demat account?
A Demat Account or Dematerialised Account provides the facility of holding shares and securities in an electronic format. During online trading, shares are bought and held in a Demat Account, thus, facilitating easy trade for the users. A Demat Account holds all the investments an individual makes in shares, government securities, exchange-traded funds, bonds and mutual funds in one place.
What is a trading account?
When you invest in the equity markets, you buy shares in exchange for money. The shares bought by the investors are stored by certified depositories. These depositories provide unique demat accounts to investors that store their stock holdings securely. When an investor sells a share, it is removed from the demat account. The shares are stored in the demat account and the money comes from the bank account, then what role does the trading account play? The trading account is the common link between the demat account, bank account and the investor. The buying and selling of shares are facilitated by the trading account. If you want to trade in equity shares, you mandatorily have to create a trading account. If you subscribe to a public offering, you don’t need a trading account as the shares, if allotted, automatically goes to the demat account. But you will always need a trading account to sell those shares or buy other shares.
What is commodity trading?
Similar to any other market, the commodities market is either a physical or a virtual space, where interested parties can trade commodities (raw or primary products) at present or future date. The price is dictated by the economic principles of supply and demand.
Types of commodities traded in India (Multi Commodity Exchange of India – MCX)
- Agricultural commodities: Black pepper, castor seed, crude palm oil, cardamom, cotton, mentha oil, rubber, Palmolein.
- Energy:Natural gas, Crude oil.
- Base Metals: Brass, Aluminium, Lead, Copper, Zinc, Nickel.
- Bullion: Gold, Silver.Types of commodities traded in India (National Commodity and Derivatives Exchange – NCDEX):
- Cereals and pulses: Maize Kharif/south, Maize rabi, Barley, Wheat, Chana, Moong, Paddy (basmati).
- Soft: Sugar.
- Fibres: Kappa’s, Cotton, Guar seed, Guar gum.
- Spices: Pepper, Jeera, Turmeric, CorianderOil and Oil seeds: Castor seed, Soybean, Mustard seed, Cottonseed oil cake, Refined soy oil, Crude palm oil.
Types of commodities traded in India (National Commodity and Derivatives Exchange – NCDEX):
- Cereals and pulses: Maize Kharif/south, Maize rabi, Barley, Wheat, Chana, Moong, Paddy (basmati).
- Soft: Sugar.
- Fibres: Kappa’s, Cotton, Guar seed, Guar gum.
- Spices: Pepper, Jeera, Turmeric, CorianderOil and Oil seeds: Castor seed, Soybean, Mustard seed, Cottonseed oil cake, Refined soy oil, Crude palm oil.
India has six major commodity trading exchanges, namely,
National Multi Commodity Exchange India (NMCE)
National Commodity and Derivative Exchange (NCDEX)
Multi Commodity Exchange of India (MCX)
Indian Commodity Exchange (ICEX)
National Stock Exchange (NSE)
Bombay Stock Exchange (BSE)
Financial instruments traded in a Stock Market
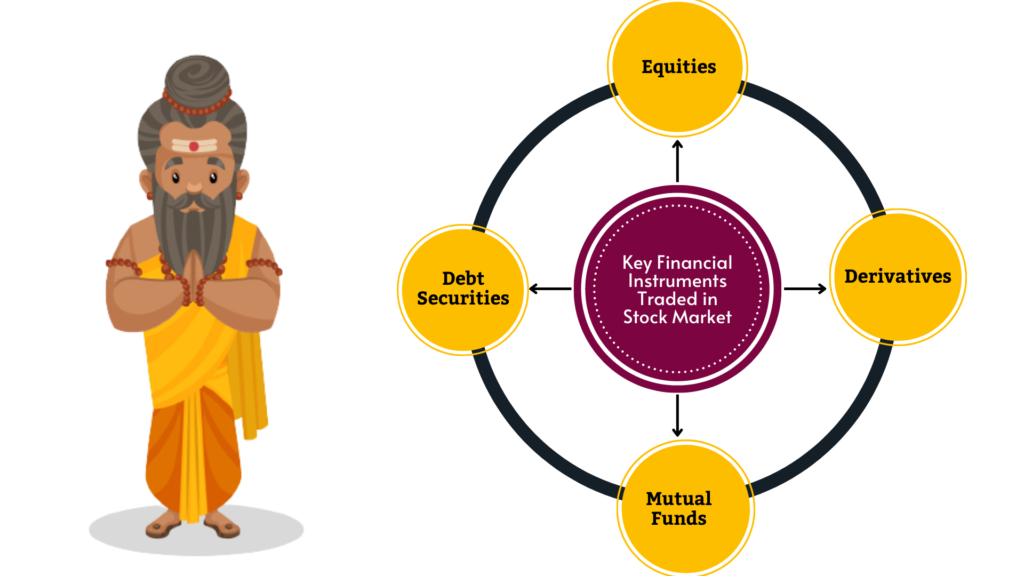
What are the financial instruments traded in a Stock Market?
Ans : – Below are the main four key financial instruments that are traded in Stock market:
Equities :- Equities are the share in the ownership of the company.
Derivatives :- These are the instruments that drives their value from an underlying asset(s).
Debt Securities :- Instruments issued by the government or companies to raise fund are Debt Securities.
Mutual Funds :- It is an instruments that collect money from a number of investors and invest the money in various assets.
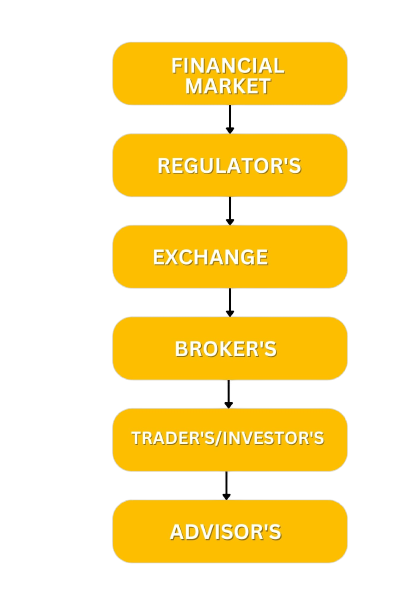
Financial markets, from the name itself, are a type of marketplace that provides an avenue for the sale and purchase of assets such as bonds, stocks, foreign exchange, and derivatives. Often, they are called by different names, including “Wall Street” and “capital market,” but all of them still mean one and the same thing. Simply put, businesses and investors can go to financial markets to raise money to grow their business and to make more money, respectively.
In India, the stock market regulator is called The Securities and Exchange Board of India, often referred to as SEBI. SEBI aims to promote the development of stock exchanges, protect the interest of retail investors, and regulate market participants’ and financial intermediaries’ activities.
An exchange is a marketplace where securities, commodities, derivatives and other financial instruments are traded. The core function of an exchange is to ensure fair and orderly trading and the efficient dissemination of price information for any securities trading on that exchange. Exchanges give companies, governments, and other groups a platform from which to sell securities to the investing public.
A broker’s prime responsibility is to bring sellers and buyers together and thus a broker is the third-person facilitator between a buyer and a seller. An example would be a real estate or stock broker who facilitates the sale of a property.
A trader is an individual who engages in the buying and selling of financial assets in any financial market, either for themself or on behalf of another person or institution. The main difference between a trader and an investor is the duration for which the person holds the asset. Investors tend to have a longer-term time horizon, while traders tend to hold assets for shorter periods of time to capitalize on short-term trends.
A stock advisor is an expert who can recommend the right avenues of investment after analysing not only the performance of various securities but also your risk-taking capacity and interests. Many advisors register with the Securities & Exchange Board of India (SEBI) and are given a registration number.
